What's New

Welcoming Dr. Jhoan Toro-Mendoza to ACS Omega
The ACS Omega team welcomes its newest Publishing Editor, Dr. Jhoan Toro-Mendoza. Dr. Toro-Mendoza brings several years of research experience in the highly interdisciplinary field of soft matter science, including as a group leader, and has served as Head of the Center for Interdisciplinary Studies of Physics at the Venezuelan Institute for Scientific Research, from where he originally obtained his Ph.D. in Physics.
Jhoan will work alongside Drs. Paul Goring and Silvia Imberti and play an important role in the publishing process by collaborating with colleagues, editors, authors, and reviewers to manage the peer-review process. This role is essential with the impressive growth in submissions at ACS Omega. Jhoan is currently based in Spain but will relocate to Oxford, UK, in 2022.
ACS Omega - In The News
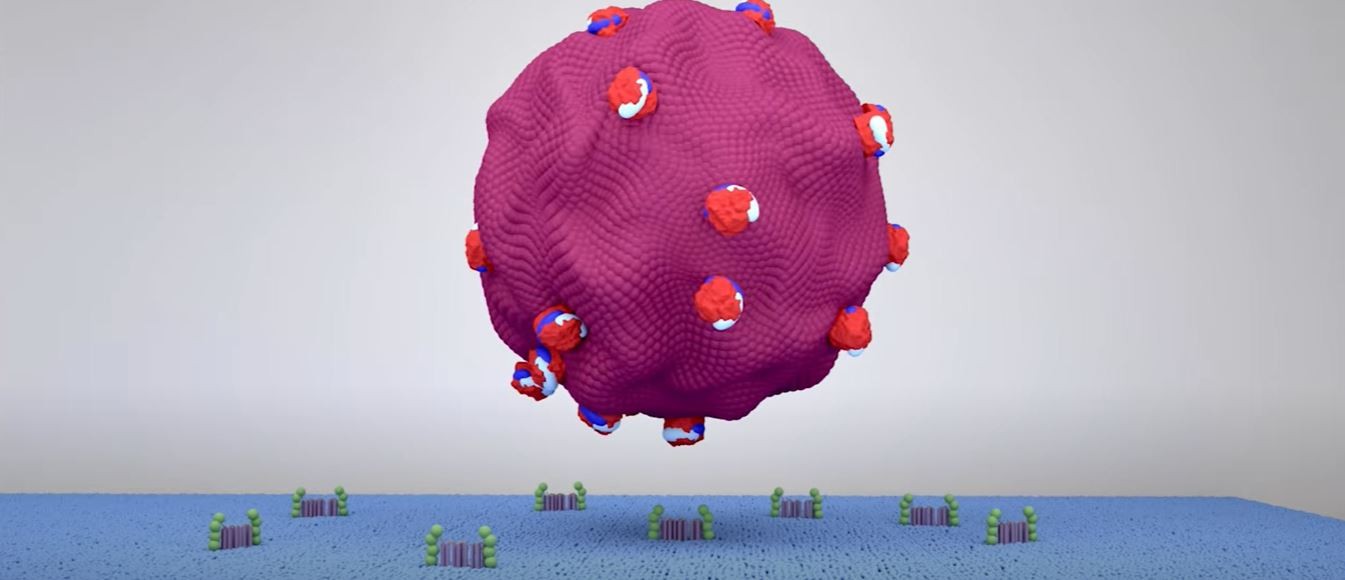
An ACS Omega publication has been picked up recently by several Brazilian news outlets, including Revista Galileu. The study is a collaboration between Prof. Ricardo Sobhie Diaz at the retrovirology department and Prof. Francisco E. G. Guimarães from the physics department at the Universidade de São Paulo (USP), as well as colleagues from the United Kingdom.
Reference: Mohammad Sadraeian et al., Photoinduced Photosensitizer–Antibody Conjugates Kill HIV Env-Expressing Cells, Also Inactivating HIV, ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25, 16524–16534
Key Journal Metrics
- ACS Omega published 296 articles in the month of August 2021, for a total of 2,197 YTD.
- Articles published by ACS Omega were downloaded 551,102 times in August, a 69% increase in usage compared to August 2020, and brings the total YTD usage for ACS Omega articles to 4,436,963.
Published Issues
pp. 21194-21842
pp. 20722-21193
pp. 20091-20721
pp. 19343-20090
Featured Articles
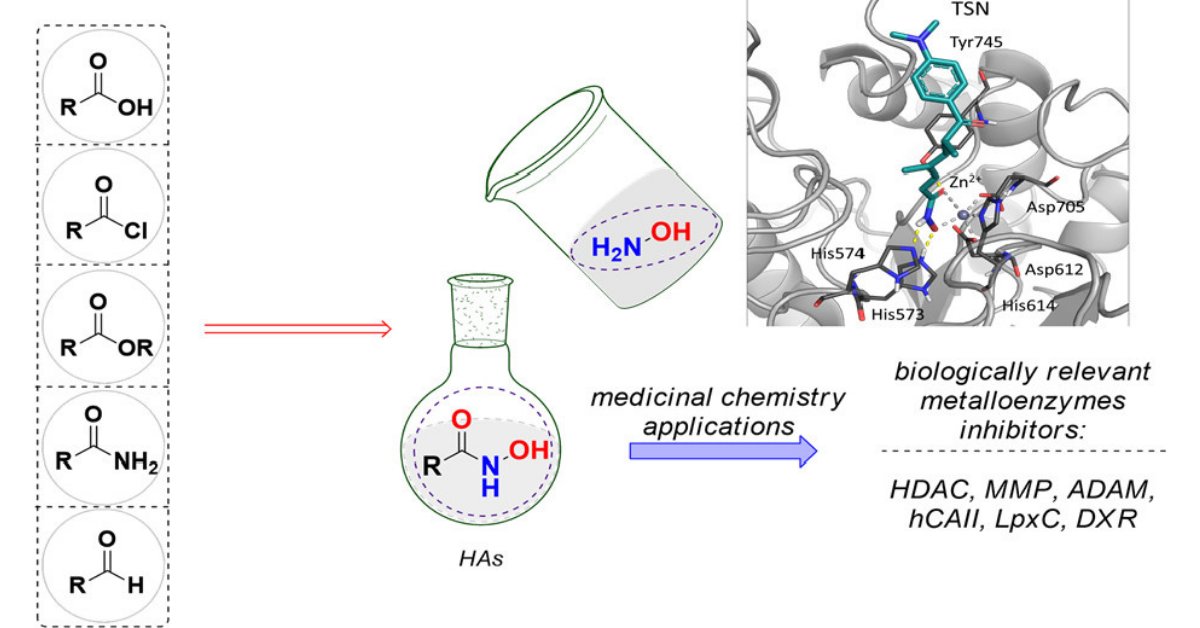
Andrea Citarella, Davide Moi, Luca Pinzi, Davide Bonanni, and Giulio Rastelli*
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 34, 21843–21849
Hydroxamic acid-based HDAC inhibitors have been relatively recently approved as anticancer drugs. In this work their physicochemical characteristics are described, as well as the most relevant methods for the introduction of such moiety into organic substrates and an overview of their uses in medicinal chemistry.
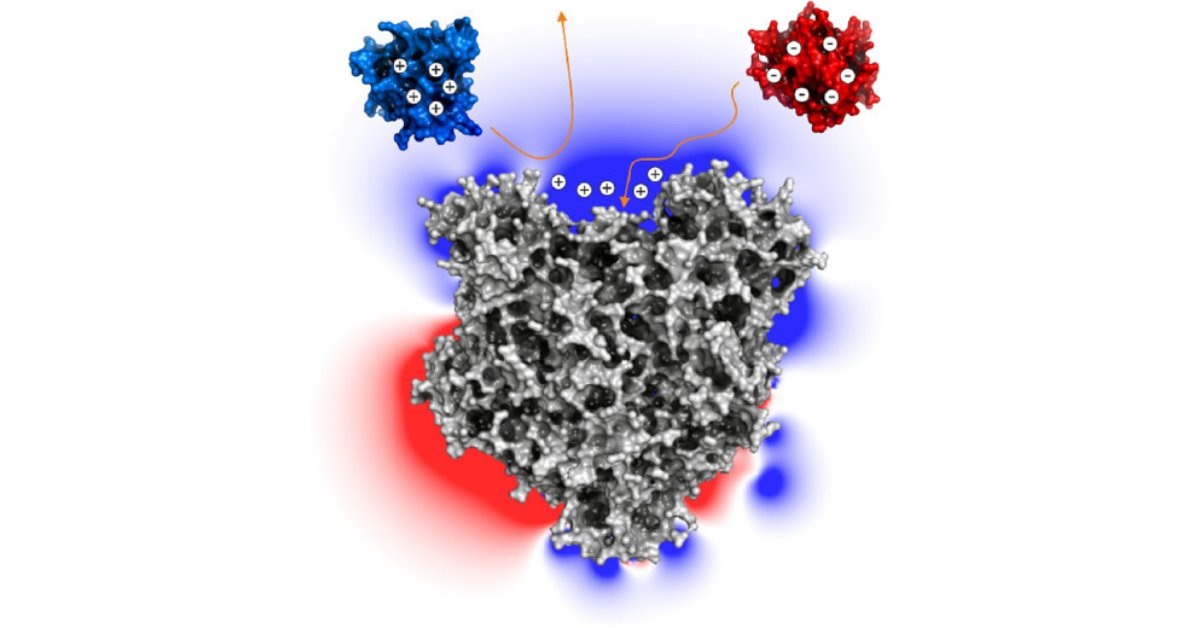
Andreas Dietl*, Thomas R.M. Barends* et al. from the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg (Germany)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33, 21457–21464
A computational approach has been taken to analyze in detail the anaerobic ammonium oxidation process in a model organism. This study illustrates one way in which cytochrome c proteins achieve specificity when carrying electrons to/from the enzymes that catalyze anammox reactions.
Suprakas Sinha Ray* et al. from the DSI-CSIR Nanotechnology Innovation Centre in Pretoria and
the University of Johannesburg (South Africa)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32, 21005–21015
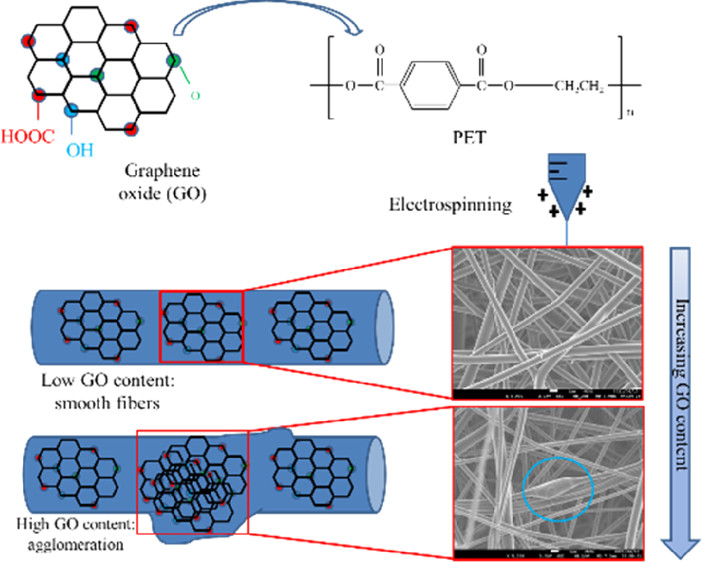
Electrospinning has become one of the most efficient and cost-effective nanofiber processing techniques, especially when it comes to the use of recycled material, such as post-consumer PET bottles. This study investigates the influence of graphene oxide as a nanofiller on the properties of electrospun recycled PET composite nanofiber membranes.
David S. Boyle* et al. from PATH, Seattle (United States)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31, 20139–20148
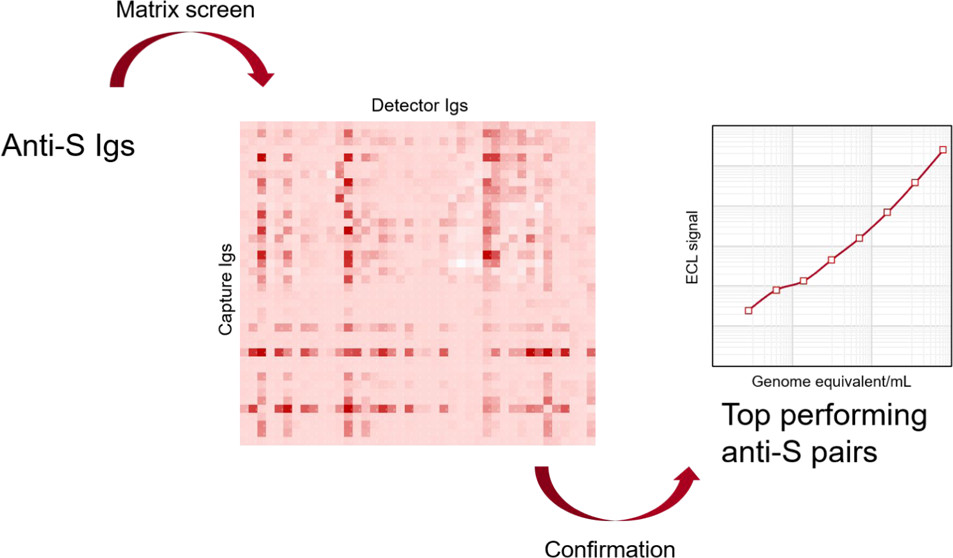
Low- and middle-income countries typically have very limited access to molecular diagnostic testing due to fewer resources. Serologic testing is an inappropriate surrogate as the early stages of infection are not detected and misdiagnosis will promote continued transmission. This work describes the development of direct antigen testing that may allow earlier diagnosis.
Manjusri Misra*, Amar K. Mohanty* et al. from the University of Guelph (Canada)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31, 20103–20111
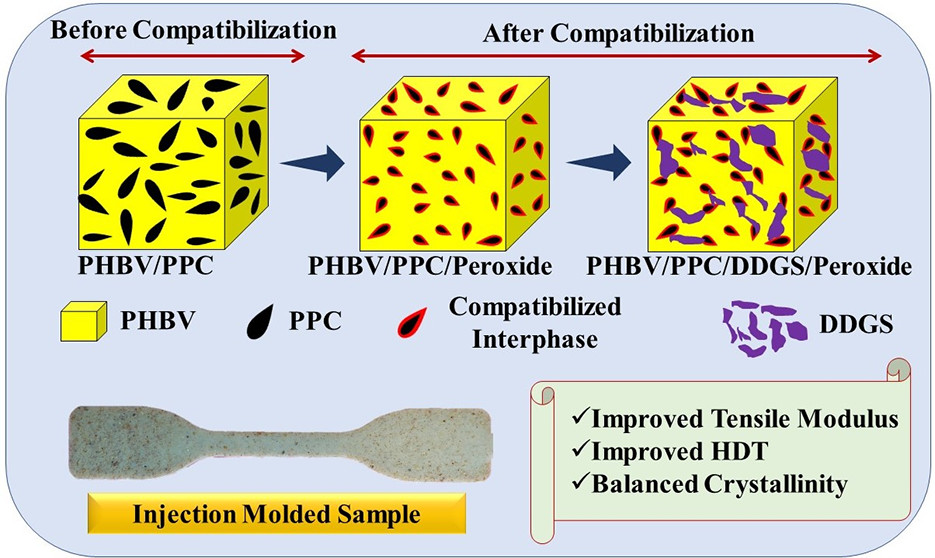
PHBV is one of the most well-known biodegradable plastics in the poly(hydroxyalkanoate) (PHA) family, is marine biodegradable, and is suitable to replace single-use plastics. However, it is expensive compared to other commercial plastics. In this article, a new PHBV/PPC blend is prepared and tested with promising results.
Ismail Ocsoy* et al. from the Erciyes University (Turkey)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31, 20637–20643
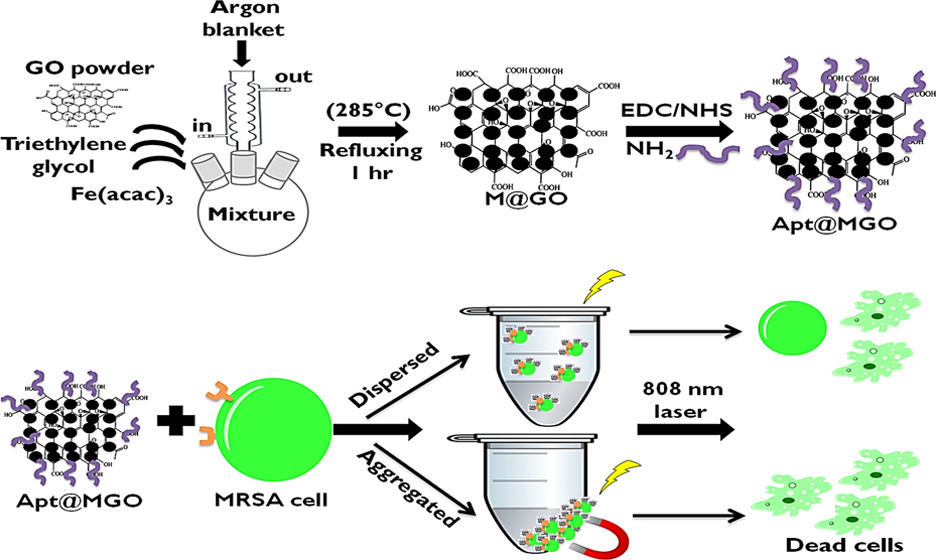
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a nosocomial and multidrug resistance bacterium that shows resistance to β-lactam antibiotics. In this in vitro study, DNA aptamer-conjugated magnetic graphene oxide is proven to be a targeted, biocompatible, and light-activated photothermal agent for efficient and rapid killing of MRSA in the aggregated state under NIR light.
Dawn E. Riegner* et al. from the United States Military Academy, West Point, New York
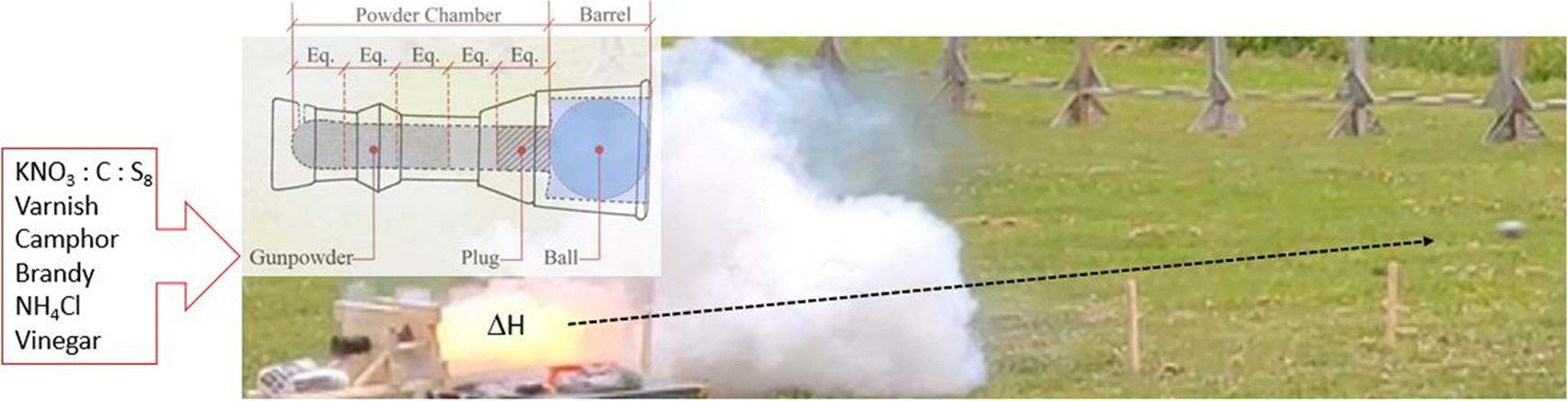
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35, 22848–22856
Gunpowder, also known as black powder, is only humanity’s second great experiment (after fire) with harnessing chemical energy. In this study, several gunpowder recipes have been examined with the aim of providing important technical information on the early manufacturing of gunpowder and of aiding historians in their interpretation of medieval texts.
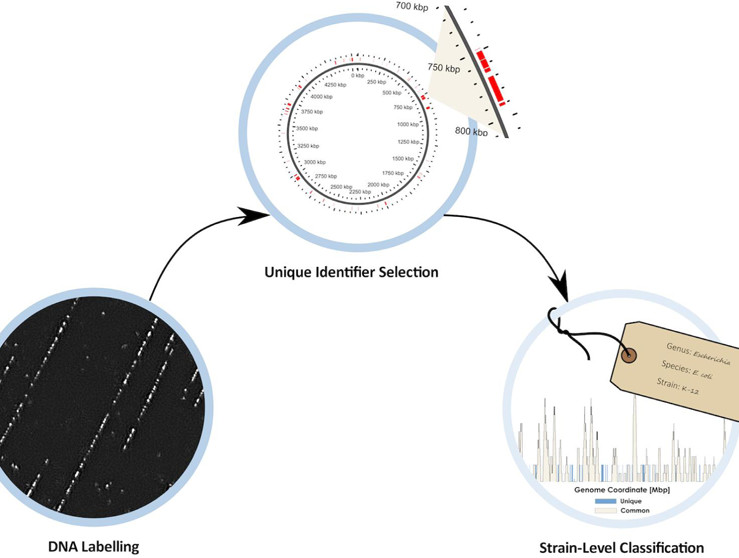
Johan Hofkens* et al. from KU Leuven (Belgium)
ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33, 21276–21283
When no functional information at the gene level is required, targeting of the 16S rRNA gene with amplicon sequencing has been a mainstay for sample composition profiling due to its short sample-to-result time and low cost compared to that of the far more expensive whole-genome sequencing. However, there is a very large resolution gap between amplicon sequencing (genus to species level) and WGS (single-gene and functional levels). This article proposes DNA optical mapping as an inexpensive and rapid complementary approach to existing sequencing modalities.
Previous Newsletters
Click below to view a previous ACS Omega Monthly Update
© 2024 American Chemical Society, 1155 16th St NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. View our Privacy Policy