What's New
In collaboration with six ACS journals, ACS Omega announces the launch of its latest Virtual Issue, From Biosensors to Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering: Open Biomaterials Research.
The theme of Biomaterials is intrinsically cross-disciplinary. Therefore, the continuous exchange of information among researchers of different backgrounds – whether in the medical, engineering, materials, physical or chemical sciences – is crucial. Freely accessible research cuts across the boundaries of disciplines and allows a much greater circulation of ideas and results.
This Virtual Issue showcases an outstanding collection of high-quality, impactful, free-to-read articles published in ACS Omega, ACS Applied Bio Materials, ACS Applied Polymer Materials, ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, ACS Macro Letters, Biomacromolecules and Macromolecules.
Topics discussed in this collection include the 3D-printing of structure-controlled antigen nanoparticles for vaccine delivery, the elasticity and viscosity of DNA liquid crystals, intelligent nanoparticle-based dressings for bacterial wound infections, and more.

Welcoming Dr. Aditi Jain to the ACS Omega team
We are delighted to welcome a new team member, Dr. Aditi Jain, who will work out of the ACS International office in New Delhi, India. Aditi joined ACS Publications in 2020 as Development Editor for JACS and ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Prior to that, Aditi, obtained her Ph.D. in BioSystems Science & Engineering at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, India (Advisor: Prof. Kaushik Chatterjee), her M.Sc. in Biotechnology at IIT Bombay, India and her B.Sc. (Honors) in Chemistry at the University of Delhi, India.
ACS Omega - In The News
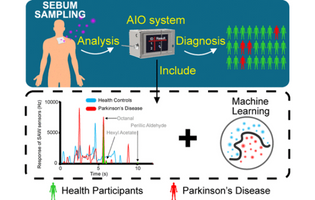
A couple of years ago, a woman named Joy Milne made headlines when scientists discovered that she could “smell” Parkinson’s disease (PD) on people with the neurodegenerative disorder. Since then, researchers have been trying to build devices that could diagnose PD through odor compounds on the skin. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Omega have developed a portable, artificially intelligent olfactory system, or “e-nose,” that could someday diagnose the disease in a doctor’s office.
Reference: Jun Liu, and Xing Chen et al., Artificial Intelligent Olfactory System for the Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease, ACS Omega (2022), DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05060
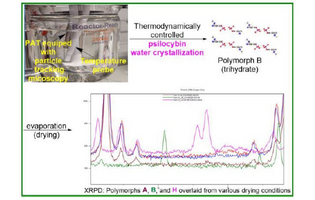
Usona Institute identifies the most favorable environments to achieve consistency and reproducibility of pharmaceutical psilocybin produced at large scale. The ability of a unique crystalline arrangement to solidify in more than one form, called polymorphs, can be optimized using precise combinations of engineering controls including temperature, cooling rate, saturation, stirring speed, and drying mode.
BusinessWire - Usona Identifies Controlled Crystal Engineering Process for Large-Scale Synthesis of Psilocybin Polymorphs
Reference: Robert B. Kargbo et al., Psilocybin: Characterization of the Metastable Zone Width (MSZW), Control of Anhydrous Polymorphs, and Particle Size Distribution (PSD), ACS Omega (2022), DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06708
Key Journal Metrics
- ACS Omega published 315 articles in the month of February 2022.
- Articles published by ACS Omega were downloaded 631,202 times in February, which represents a 34% increase in usage compared to the equivalent time period in 2021.
Published Issues
Vol. 7 Issue 7, pp. 5605-6436
Vol. 7 Issue 6, pp. 4724-5604
Vol. 7 Issue 5, pp. 3836-4723
Vol. 7 Issue 4, pp. 3134-3835
Featured Articles
It has previously been demonstrated that native chemical Turing machines can be constructed by exploiting the nonlinear dynamics of the homogeneous oscillating Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction. In this article, a carefully designed system is presented that can perform Chomsky type 1 CSL word recognition and its power is demonstrated through the testing of a series of in-language and out-of-language words.
Juan Pérez-Mercader et al., Harvard University, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7, 6099–6103
The study of the physicochemical properties of electrolytes is never straightforward. However, by using a very simple molecular picture for water-in-salt electrolytes, the authors proposed a theoretical model that may be used to relate electrochemical properties of water-in-LiTFSI electrolyte to intermolecular interactions.
Oksana Patsahan, National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Lviv, Ukraine
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6655-6664
Artificial electronic skin (e-Skin) is an electronic sensor that can simulate human skin’s basic perception by responding to changes in resistance or capacitance while maintaining key features such as low thickness, extensibility, and compliance. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), is one of the widely used supporting materials of e-Skin. In this work, a flexible strain sensor, based on improved PDMS, with adjustable mechanical properties and electrical properties is presented.
Bin Dong, Xiuling Liu et al., Hebei University, China
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7, 5825–5835
With the escalating demand for sustainable energy sources, the sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) appear as a pragmatic option to develop large energy storage grid applications in contrast to existing lithium-ion batteries owing to the availability of cheap sodium precursors. The insights provided in the current review may serve as an aid in designing efficient cathode materials for state-of-the-art SIBs.
Suddhasatwa Basu et al., Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, India
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7, 5605–5614
The amide/peptide bond is almost exclusive in peptide structures, but its presence is also the most common in organic compounds with pharmaceutical interest. However, after September 11, 2001, the potentially explosive character of HOBt and its triazole/triazine-related additives was reported. In this context, this group started a broad research project with the goal of developing another family of safe and efficient additives, based on a different template.
Beatriz G. de la Torre, Fernando Albericio et al., University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7, 6007–6023
Bacillus cereus is a pathogenic bacterium, Gram-positive, aerobic, and facultative anaerobic that can produce spores and different toxins; it is involved in serious foodborne illnesses. This work is aimed to study the potency of electroactivated solutions (EAS) of calcium lactate, calcium ascorbate, and their mixture as antibacterial agents against B. cereus ATCC 14579 vegetative cells.
Mohammed Aider et al., Université Laval, Quebec, Canada
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4, 3579–3595
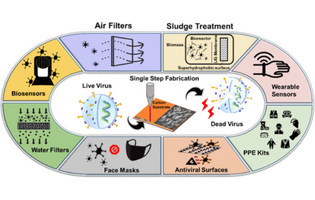
This perspective highlights state-of-the-art and the future possibilities on LIG for its antimicrobial, antiviral, anti-biofouling, and sensing applications. It also suggests avenues for the incorporation of LIG into air purifiers, antiviral surfaces, wearable sensors, water filters, sludge treatment, and biosensing.
Swatantra P. Singh et al., Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Mumbai, India
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6, 5112–5130
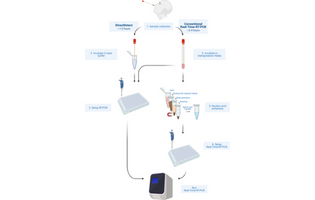
This preliminary study evaluated a novel SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic test called DirectDetect SARS-CoV-2 Direct Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) based on a limited sample size of 24 respiratory samples from 14 SARS-CoV-2-positive patients. The test is advantageous compared to others on the market since it does not require viral transport medium or viral RNA extraction prior to nucleic acid amplification and detection.
Anubhav Tripathi et al., Brown University, Rhode Island, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6, 4945–4955
Previous Newsletters
Click below to view a previous ACS Omega Monthly Update
© 2024 American Chemical Society, 1155 16th St NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. View our Privacy Policy