What's New

In April, we traditionally celebrate our excellent pool of reviewers for their invaluable voluntary support in serving the journal and for their assistance in maintaining the high quality of ACS Omega's published content. We take this opportunity to extend a special thank you to our EAB members, who often serve as reviewers and adjudicators.
As a small thank you for your continued support, we have created a series of ACS Omega-branded Zoom backgrounds for you to use at your discretion.
Click on the images below to download them.
Virtual Issues: 40 Years of GenBank and Prevention and Treatment of Malaria
ACS Omega participated in two new Virtual collections by ACS Publications:
- 40 Years of GenBank, celebrating DNA day (April 25) GenBank, the European Nucleotide Archive and the DNA DataBank of Japan. The existence and ongoing expert curation of publicly available DNA databases has transformed scientific research, and has enabled new insights into mechanisms of disease, protein evolution, biosynthetic gene clusters, and much more.
- Prevention and Treatment of Malaria, presenting recent (2017-present) advances in treatment and prevention of malaria in recognition of World Malaria Day on April 25. Every year, malaria results in more than 400,000 deaths worldwide.
Key Journal Metrics
- ACS Omega published 332 articles in April, for a total of 1,357 YTD. As compared to the equivalent timeframe in 2021, this represents a 22.9% increase in published output.
- Articles published by ACS Omega were downloaded 750,039 times in April, which represents a 32% increase in usage compared to the equivalent time period in 2021.
Published Issues
April 5, 2022, Volume 7, Issue 13 pp. 10854-11520
April 12, 2022, Vol. 7 Issue 14 pp. 11521-12447
April 19, 2022 Vol. 7 Issue 15 pp. 12448-13397
April 26, 2022 Vol. 7 Issue 16 pp. 13398-14401
Featured Articles
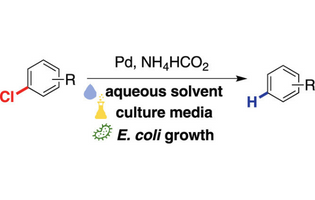
Developing nonenzymatic chemistry that is nontoxic to microbial organisms creates the potential to integrate synthetic chemistry with metabolism and offers new remediation strategies. Chlorinated organic compounds known to bioaccumulate and cause harmful environmental impact can be converted into less damaging derivatives through hydrodehalogenation.
Erica E. Schultz* et al., Lake Forest College, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18, 16028–16034
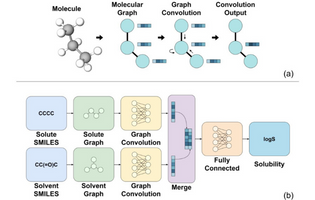
Solubility prediction of organic solutes plays an important role in pharmaceutical industries. This paper illustrates how machine learning concepts can be used to predict the solubility of organic solutes in several solvents. Moreover, the paper also sheds light on the use of machine learning and deep learning algorithms in chemical thermodynamics.
Sumin Lee et al., Polymer Research Lab, Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology and Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 14, 12268–12277
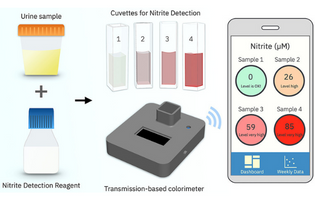
This paper reports on a low-cost, quantitative, point-of-care solution for the early detection of nitrite, a common biomarker for urinary tract infections (UTIs). This portable analyzer can be expanded to other colorimetric-based chemistries to detect a panel of biomarkers, which can improve the overall sensitivity and specificity of the desired assay.
Vince S. Siu*, et al. IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, New York, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 13, 11126–11134
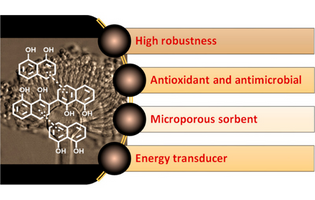
Melanins are a wide class of natural pigments biosynthesized by different kinds of living organisms throughout all of the life domains, from bacteria to fungi, plants, and mammals. The biological functions played by these natural pigments are different (i.e., camouflage, radioprotection, thermoregulation) and ascribable to a peculiar set of physical–chemical properties making melanins a unique class of biopolymers.
Valeria Lino and Paola Manini*, University of Napoli Federico II, Italy
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18, 15308–15314
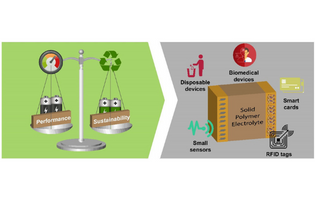
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are the most widely used energy storage system because of their high energy density and power, robustness, and reversibility, but they typically include an electrolyte solution composed of flammable organic solvents, leading to safety risks and reliability concerns for high-energy-density batteries. A step forward in Li-ion technology is the development of solid-state batteries suitable in terms of energy density and safety for the next generation of smart, safe, and high-performance batteries.
João C. Barbosa, et al., University of Minho, Portugal and BCMaterials, Basque Center for Materials, Spain
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 17, 14457–14464
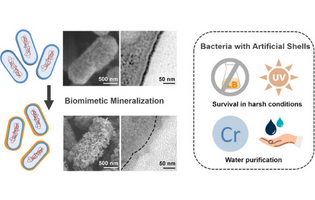
This paper reports on a microfluidics-based biomimetic mineralization method to encapsulate bacteria (e.g., Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis) with zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8). The artificial shells endowed bacteria with the ability to tolerate harsh environments, which was significant during the treatment of contaminated water.
Rongbing Tang, et al.
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18, 15385–15395
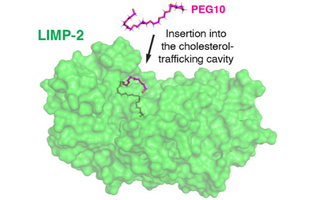
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is the most prominent clinically administered synthetic polymer, because it has low affinity for most proteins. However, since it has such low affinity for most proteins, little is known about how it interacts with proteins. This paper demonstrates that the oxygens of PEG bind residues with high hydrogen bonding capabilities. However, the PEG–protein interaction is likely to be transient unless groups of resides can clamp down on PEG or a cavity that at least part of the PEG chain can enter is in close proximity to lower PEG’s entropy.
Paul Dalhaimer* and Kate R. Blankenship, University of Tennessee, United States
ACS Omega 2022, 7, 18, 15728–15738
Previous Newsletters
Click below to view a previous ACS Omega Monthly Update
© 2024 American Chemical Society, 1155 16th St NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA. View our Privacy Policy